Exporting from and Importing into the IBB table
This article guides you step by step through both importing and exporting: how to export an IBB (Intelligent Bid Book) table to CSV and how to import data into an IBB table.

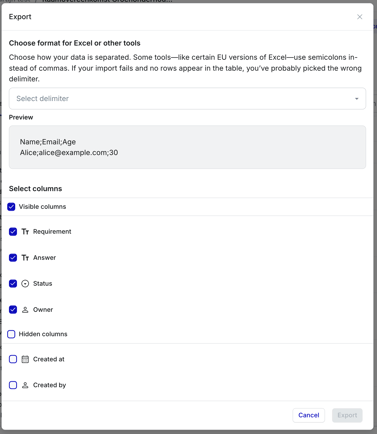
Exporting the IBB table to .csv
- Open any IBB table.
- Click the three dots on the top right, then Export to .csv.
- Choose the delimiter you want to use.
- Choose columns to include (by default it selects all visible columns + highlight information)
- Download starts
- CSV export flattens every property - boolean, tag, and user fields - into a plain-text column.


How to import CSV into an Existing Table
- In the target table, click the three dots on the top right then Import data.
- Upload a CSV (often the same file previously exported & enriched).
- Choose the delimiter you want to use. Be aware that Numbers (Mac) will always change the delimiter to semicolon once you export the file.
- After uploading the CSV, choose the matching IBB column for each CSV header (no auto-suggestions are provided)
- Only text‑type columns are eligible → unmatched/unsupported columns ignored.
- New rows are appended; existing rows remain unchanged (no merge/overwrite).
When working with CSV files, the delimiter determines how columns are separated in the file. The most common delimiter is a comma (,), but not all tools or regions use the same standard. For example, some European versions of Excel—especially those using a comma as the decimal separator—default to using a semicolon (;) as the delimiter.
To ensure that IBB data is displayed and interpreted correctly when opened in tools like Excel or re-imported into IBB, we give users the option to explicitly choose the delimiter. This prevents formatting issues, like data ending up in a single column or breaking the structure of the table.
How to work with .csv?
When you open a CSV file and all the data appears in a single column, this is usually due to a delimiter mismatch. Here’s how to fix it:
Open a CSV and split the content into separate columns in Excel:
- Open Excel and go to the “Data” tab.
- Click “From Text/CSV” and select your CSV file.
- Excel will show a preview. Choose the correct delimiter (comma or semicolon, depending on your region/tool).
- Click “Load” to import the data into separate columns.
If you’ve already opened the file and see everything in one column:
- Select the column.
- Go to “Data” > “Text to Columns”.
- Choose “Delimited”, click Next.
- Select the correct delimiter (comma or semicolon), click Finish.
Not sure which delimiter to use? Try opening the file in a text editor first (like Notepad or VS Code) to check what separates the columns
.png?width=100&height=75&name=Logo%20wit%20(1).png)